Downloads
Legionnaires' Thermometer Kits
Description
Incorrect water temperature is a key risk factor for Legionella growth. The Legionella bacteria multiply in water at temperatures between 20 to 45 °C. A typical method of control is to store hot water above 60°C and distribute it at above 50°C (care must be taken to prevent scalding). Cold water should be kept below 20 °C. The biggest risk is during holiday periods, were a building’s water systems can be left ideal for several days. The water left in pipes during this period can be where the most risk occurs.
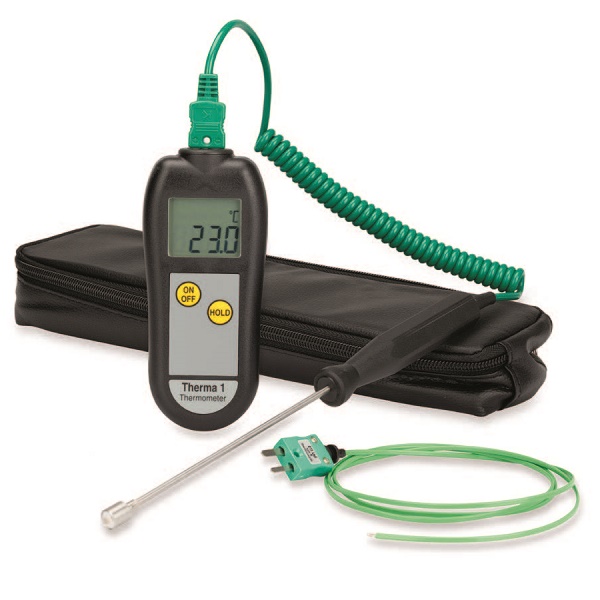
Legionnaires Standard Kit contains all of the following:
- Therma 1 thermometer (Part Ref: 221-041)
- Waterproof Surface Immersion Probe (Part Ref: 323-046)
- Heavy-Duty PFA wire probe (Part Ref: 133-372)
- Zip Pouch (Part Ref: 830-037)
LEGAL RESPONSIBILITIES FOR TESTING FOR LEGIONELLA
As an employer or the person in control of premises, it’s your legal responsibility to conduct a risk assessment for exposure to legionella. The revised Approved Code of Practice (ACOP) Legionnaires’ disease: Control of Legionella Bacteria in water systems (L8), issued by the Government’s Health and Safety Executive (HSE), ex-tends the guidance on controlling legionella bacteria in water systems. The code applies to all hot and cold water systems in the workplace, regardless of their capacity. While domestic systems may pose a risk, the code only applies to risks arising from work activities. However, it does include domestic landlords who have a responsibility to keep their tenants safe from health hazards. This means that all employers and landlords who manage premises with hot/cold water systems and/or wet cooling systems must identify any risk of contamination and take steps to prevent or control it.