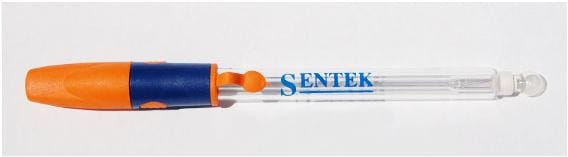
Description
pH Electrode Theory
pH electrode measurements are made by comparing the readings in a sample with the readings in standards whose pH has been defined. When a pH sensing electrode comes in contact with a sample, a potential develops across the sensing membrane surface and that membrane potential varies with pH levels. A reference electrode provides a second, unvarying potential to quantitatively compare the changes of the sensing membrane potential. Combination pH electrodes are composed of a sensing electrode with the reference electrode built into the same electrode body. Combination electrodes provide the same selectivity and response as a half-cell system, but offer the convenience of working and maintaining only one electrode. The difference between the reference electrode and sensing electrode potentials is in millivolts, which can be amplified by a suitable pH amplifier/signal convertor. This will then provide a mA or V output that can be converted to pH units on a suitable display or logging unit.
The section below provides the basic information for a selection of standard pH electrode for your applications. Additional details can be found on the individual product datasheets and a selection guide is available in the downloads section.